Lead Nitrate Molecular Formula
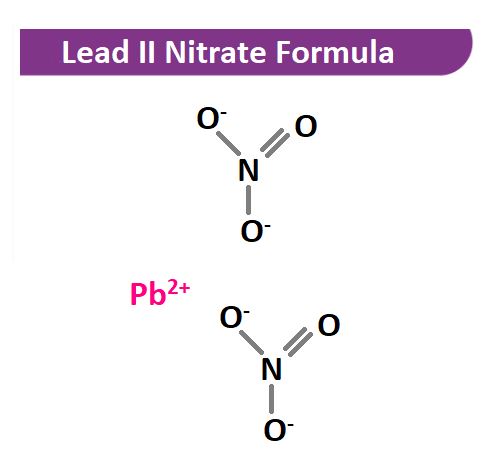
The molecular formula for lead nitrate is Pb(NO3)2. This chemical compound consists of one lead (Pb) atom, two nitrogen (N) atoms, and six oxygen (O) atoms. Lead nitrate is a white crystalline solid that is highly soluble in water and is often used in various applications, including the production of matches, fireworks, and other pyrotechnic devices.
Chemical Structure
The chemical structure of lead nitrate can be represented as follows:
Pb²⁺ + 2NO₃⁻ → Pb(NO₃)₂
In this structure, the lead atom (Pb) is bonded to two nitrate ions (NO₃⁻), resulting in a stable and highly soluble compound.
Properties
Lead nitrate has several distinct properties that make it useful in a variety of applications. Some of its key properties include:
- Molecular weight: 331.2 g/mol
- Density: 4.53 g/cm³
- Melting point: 270-290°C (dec.)
- Solubility: Highly soluble in water ( > 50 g/100 mL)
- Toxicity: Highly toxic, can cause lead poisoning if ingested or inhaled
Uses
Lead nitrate has several important uses, including:
- Pyrotechnics: Lead nitrate is used as an oxidizer in the production of matches, fireworks, and other pyrotechnic devices.
- Laboratory reagent: Lead nitrate is used as a reagent in various laboratory tests, including the detection of sulfide ions and the preparation of lead-based compounds.
- Photography: Lead nitrate is used in some photographic developers and fixers.
- Textile industry: Lead nitrate is used as a mordant in the textile industry to fix dyes and improve colorfastness.
Safety Precautions
While lead nitrate has several important uses, it is also highly toxic and requires special handling and safety precautions. Some of the key safety precautions include:
- Wearing protective clothing: Wear gloves, goggles, and a face mask when handling lead nitrate to prevent skin contact and inhalation.
- Avoiding ingestion: Avoid ingesting lead nitrate, as it can cause lead poisoning.
- Proper disposal: Dispose of lead nitrate and any contaminated materials according to local regulations and guidelines.
Environmental Impact
Lead nitrate can also have significant environmental impacts, including:
- Water pollution: Lead nitrate can contaminate water sources and harm aquatic life.
- Soil pollution: Lead nitrate can persist in soil for long periods, posing a risk to plants and animals.
- Air pollution: Lead nitrate can release toxic fumes during decomposition, contributing to air pollution.
To minimize the environmental impacts of lead nitrate, it is essential to handle and dispose of the substance properly, following local regulations and guidelines.
Conclusion
In conclusion, lead nitrate is a highly toxic and versatile compound with various applications, including pyrotechnics, laboratory reagents, photography, and the textile industry. However, its toxicity requires special handling and safety precautions to minimize the risk of exposure and poisoning. By understanding the properties, uses, and safety precautions associated with lead nitrate, we can minimize its environmental impacts and ensure safe handling and disposal.
What is the molecular formula for lead nitrate?
+The molecular formula for lead nitrate is Pb(NO₃)₂.
What are the key properties of lead nitrate?
+Lead nitrate has a molecular weight of 331.2 g/mol, a density of 4.53 g/cm³, and a melting point of 270-290°C (dec.). It is highly soluble in water and highly toxic.
What are the uses of lead nitrate?
+Lead nitrate is used in pyrotechnics, laboratory reagents, photography, and the textile industry.

