12 Enthalpy Calculator Tips For Easy Solutions
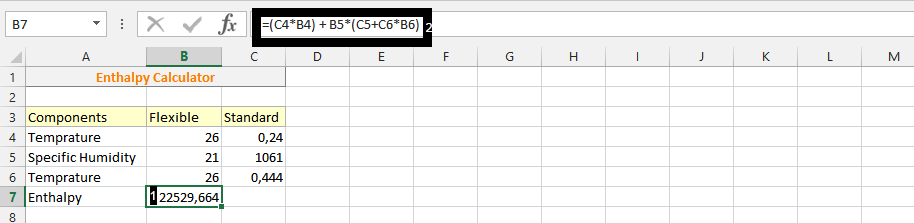
Enthalpy, a fundamental concept in thermodynamics, represents the total energy of a system, including its internal energy and the energy associated with the pressure and volume of a system. Calculating enthalpy is crucial in various fields, such as chemistry, physics, and engineering, as it helps in understanding and predicting the behavior of systems under different conditions. An enthalpy calculator is a tool designed to simplify the process of calculating enthalpy, making it easier to solve problems related to thermodynamic processes. Here are 12 tips for using an enthalpy calculator to find easy solutions to your thermodynamic problems:
1. Understanding Enthalpy
Before diving into calculations, ensure you understand what enthalpy is and its significance in thermodynamic processes. Enthalpy (H) is calculated using the formula H = U + pV, where U is the internal energy, p is the pressure, and V is the volume of the system.
2. Choosing the Right Calculator
Select an enthalpy calculator that fits your needs. There are various calculators available online, each with its own set of features. Some calculators may be more suited for simple calculations, while others can handle more complex thermodynamic equations.
3. Inputting Values Correctly
When using an enthalpy calculator, it’s crucial to input the values correctly. Ensure that the units of measurement for internal energy (U), pressure (p), and volume (V) are consistent. Most calculators will specify the required units, so be sure to follow the instructions.
4. Converting Units
Sometimes, the values you have might be in different units than what the calculator requires. Be prepared to convert these units. For example, if your pressure is in atmospheres (atm) but the calculator requires pascals (Pa), you’ll need to perform the conversion (1 atm = 101,325 Pa).
5. Calculating Internal Energy
The internal energy (U) of a system can be calculated or looked up, depending on the context of your problem. If you’re calculating the change in enthalpy, you’ll need the initial and final states’ internal energies.
6. Pressure and Volume Considerations
For calculations involving gases, the ideal gas law (PV = nRT) can be useful in finding either pressure or volume if one of the other variables is known, along with the number of moles (n) and the gas constant ® at the given temperature (T).
7. Using Enthalpy Change (ΔH)
Often, problems will ask for the change in enthalpy (ΔH) rather than the absolute enthalpy. ΔH = H_final - H_initial. This calculation is crucial in understanding the energy changes in chemical reactions or phase transitions.
8. Standard Enthalpy of Formation
For chemical reactions, the standard enthalpy of formation (ΔHf°) is a critical value. It represents the change in enthalpy when one mole of a compound is formed from its constituent elements in their standard states. These values can be found in thermodynamic tables.
9. Enthalpy of Reaction
To calculate the enthalpy of a reaction, you sum the standard enthalpies of formation of the products and subtract the sum of the standard enthalpies of formation of the reactants. This calculation can help predict whether a reaction is exothermic or endothermic.
10. Phase Transitions
Enthalpy calculations are also essential for understanding phase transitions (solid to liquid, liquid to gas). The enthalpy of fusion (melting) and enthalpy of vaporization are specific to each substance and can be used to calculate the energy required for these transitions.
11. Balancing Chemical Equations
Before calculating enthalpy changes for reactions, ensure the chemical equation is balanced. This step is crucial because the coefficients in a balanced equation tell you the relative amounts of reactants and products.
12. Practicing with Examples
The best way to become proficient in using an enthalpy calculator is by practicing with different examples. Start with simple problems and gradually move to more complex ones. This approach will not only improve your understanding of enthalpy calculations but also enhance your problem-solving skills in thermodynamics.
FAQ Section
What is the formula for calculating enthalpy?
+Enthalpy (H) is calculated using the formula H = U + pV, where U is the internal energy, p is the pressure, and V is the volume of the system.
Why is calculating enthalpy important?
+Calculating enthalpy is important because it helps in understanding and predicting the behavior of systems under different conditions, which is crucial in various fields like chemistry, physics, and engineering.
How do I choose the right enthalpy calculator for my needs?
+Choose an enthalpy calculator that fits your specific needs. Consider what features you require, such as the ability to handle complex thermodynamic equations or simplicity for basic calculations. Ensure it aligns with the level of detail and accuracy your work demands.
By following these tips and understanding the basics of enthalpy calculations, you can efficiently use an enthalpy calculator to solve a wide range of thermodynamic problems, enhancing your proficiency in this critical area of physics and chemistry. Remember, practice with various examples to solidify your understanding and improve your calculation skills.

